What is Atrial Fibrillation?
Atrial fibrillation, also known as AFib, is a condition that affects approximately four million people in the United States. Although there has been much discussion about the condition recently, many people are unaware of what atrial fibrillation truly is.
Following is a basic overview of AFib, but keep in mind that if you or someone you know is experiencing these signs, it’s important to see a cardiologist for a thorough diagnosis.
What is Atrial Fibrillation?
In some cases, individuals can live with AFib without serious complications, but in other situations it can be life-threatening.
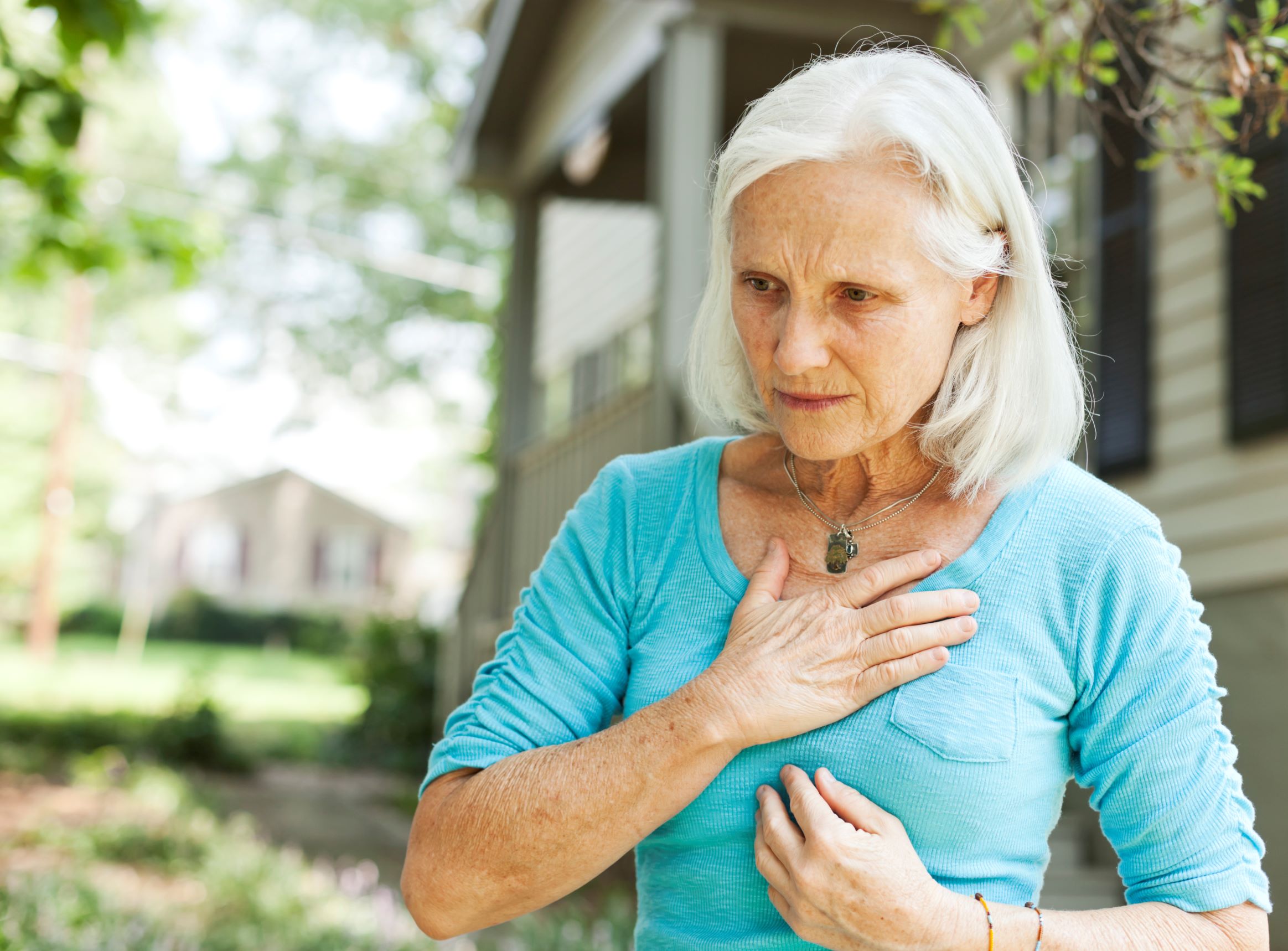
Atrial fibrillation refers to your heart beating too quickly or irregularly due to the heart’s “electrical system” not functioning the way it should. The two upper parts of the heart quiver, disrupting normal “communication” within the heart. Some cases are related to a heart valve problem.
Individuals who have atrial fibrillation may feel heart palpitations, fatigue, shortness of breath, dizziness, and chest pain.
Types of Atrial Fibrillation
These feelings can come on suddenly and last only a few seconds, or they can happen regularly for years.
There are three main types of atrial fibrillation: paroxysmal, persistent, and permanent.
Paroxysmal comes and goes and usually stops on its own, whereas persistent atrial fibrillation lasts more than a week and can become permanent.
Factors Associated with AFib
While the exact causes of atrial fibrillation are still being researched, several demographic, history, and health factors have been correlated with Afib.
Factors shown to be related to AFib or that bring on temporary AFib symptoms include:
- High blood pressure
- Previous heart attack/heart surgery
- Heart failure
- Valve disease
- Obesity
- Sleep apnea
- Hyperthyroidism
- Heredity
- Heavy alcohol consumption
- Caffeine
- Stress
Atrial Fibrillation Treatment
AFib is treated differently depending on the symptoms, severity, type of atrial fibrillation, and the health of the individual.
Treatment methods include:
- Lifestyle changes, such as managing stress and maintaining a heart-healthy diet
- Medications
- Surgical procedures or implantations, including electrical cardioversion, catheter-based ablation, surgical maze, and pacemakers
Atrial fibrillation can become life threatening if blood clots form in the chambers of the heart. These clots can travel to the brain, causing a stroke. If you or someone you know has been experiencing these signs, make an appointment to speak with one of our heart doctors in Shelby Township, Roseville, East China, or Macomb Township.